21/11/2024 0 Comments
The elasticity of connective tissue: Essential for the body
Connective tissue is one of the cornerstones of our body. It supports, connects, and protects organs, bones, and other tissues. One of the most important properties of connective tissue is elasticity, which means its ability to stretch and return to its original shape. This property is crucial for various bodily functions, from joint flexibility to the skin’s capacity to adapt to movement. But what exactly does the elasticity of connective tissue entail? And why is it so important for our health?
What is Elasticity in Connective Tissue?
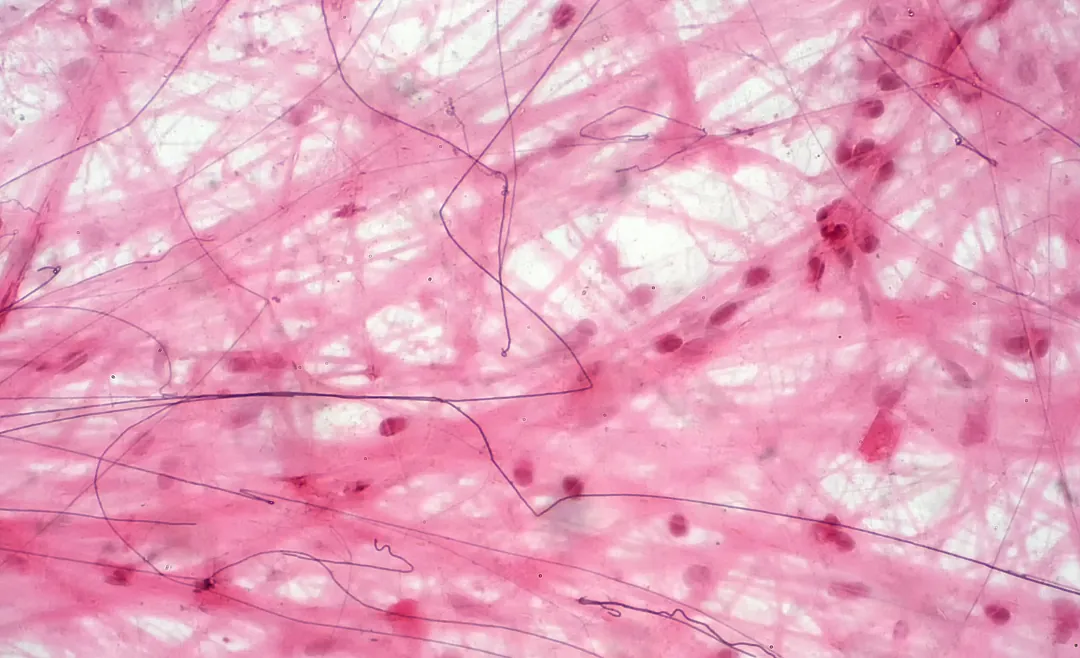
Elasticity is the ability of a material to return to its original shape after being subjected to tension or stretching. Connective tissue is made up of several types of fibers, with elastic fibers being the most important for the tissue's stretchability. In addition to elastin, many connective tissues also contain collagen, which provides strength and structure.
Elastin, a protein that is abundantly present in connective tissue, plays a key role in elasticity. When connective tissue is stretched, elastin ensures that it returns to its original form without permanent damage. This is vital for the functionality of tissues such as the skin, blood vessels, lungs, joints, and even the spine.
Functions of Elastic Connective Tissue
- Flexibility and Movement
Elastic connective tissue plays a crucial role in the flexibility of the body. Joints such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder require elastic connective tissue to move smoothly and adapt to various levels of stress. Muscles and tendons must stretch during movement, but elastic connective tissue ensures that they return to their original position afterward. - Blood Vessels and Heart Health
The walls of blood vessels, particularly arteries, contain elastic connective tissue. This allows the blood vessels to stretch when blood is pumped at high pressure (such as during heartbeats) and then contract to regulate blood flow. The elastic properties of blood vessels are essential for good circulation and help reduce the strain on the heart. - Skin and Aging
The skin also contains elastic connective tissue, primarily in the form of elastin, which enables the skin to stretch and adapt to the movements of the body. As we age, the amount of elastin in the skin decreases, leading to a loss of elasticity. This is one of the primary causes of wrinkles and sagging skin. Good skincare and a healthy lifestyle can help maintain skin elasticity, although genetics play an important role in how quickly this process occurs. - Lungs and Breathing
The lungs also contain elastic connective tissue, which is essential for their function. The elastic tissue allows the lungs to expand when air is inhaled and contract when exhaled. These elastic properties help the lungs function efficiently, enabling us to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. - Spine and Movement
The spine is supported by various types of connective tissue, including elastic connective tissue. This allows the vertebrae to move, bend, and even absorb a certain degree of compression. Elastic connective tissue in the intervertebral discs helps absorb the shocks of daily movements, such as walking and running.
Reduced Elasticity and Health Problems
Although connective tissue is elastic, this property can diminish over time due to various factors, such as aging, overuse, injury, smoking, poor diet, or genetic conditions. The loss of elasticity can lead to several health issues, including:
- Arthritis and Joint Pain: As elastic connective tissue in joints decreases, more friction can occur, leading to inflammation and pain.
- Loss of Skin Elasticity: As mentioned earlier, the decline in elastin in the skin can lead to wrinkles and sagging.
- Weakened Blood Vessels: With aging or chronic conditions, the elasticity of blood vessels can decrease, increasing the risk of high blood pressure, cardiovascular diseases, and strokes.
How to Support the Elasticity of Connective Tissue
Although the aging process is inevitable, there are several ways to support and maintain the elasticity of connective tissue:
- Healthy Diet: Nutrients such as vitamin C (important for collagen and elastin production), proteins (for building connective tissue), and healthy fats (such as omega-3 fatty acids) are essential for connective tissue health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as stretching, yoga, and strength training, can help maintain the flexibility of connective tissue. These activities improve circulation, which supports the regeneration of connective tissue.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water is crucial for connective tissue health. Connective tissue needs proper hydration to remain smooth and elastic.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking accelerates the breakdown of elastin and collagen, reducing the elasticity of connective tissue. Avoiding smoking helps keep the tissue in better condition for longer.
- Supplements: There are supplements available that support connective tissue, such as glucosamine, chondroitin, vitamin C and collagen. Consult a doctor or nutritionist before using these.
Conclusion
Elasticity in connective tissue is crucial for mobility, skin health, circulation, breathing, and more. The ability of connective tissue to stretch and return to its original state ensures that our body functions smoothly and efficiently. Maintaining this elasticity through healthy habits can help support the functions of connective tissue and prevent health problems.

Comments